www.searchtapari.in
Concrete failures at site are associated to several reasons; right from concrete mix design, properties of materials used, mixing, placing, compaction, curing procedures and many more. There are many misconceptions about the duration of curing of concrete, especially when we refer to site conditions. On many occasions, it is found that the curing period of concrete elements, plasters, brickwork, etc is left to the discretion of the site staff. Improper curing is considered as one of the significant reasons for concrete failures in columns, beams, slabs, pavements, etc, evident in the form of cracks, which are easily noticeable by the naked eyes. The vertical member like a column, in particular, is one of the most victimized RCC elements which must be carefully cured, as the entire load from the slabs and beams are supported by columns and transferred to the foundations. Unfortunately, adequate curing is not given much importance at most of the sites leading to reduction in the durability of the structure.
Curing of concrete plays a major role in developing the microstructure and pore structure of concrete. Curing of concrete means maintaining moisture inside the body of concrete during the early ages and beyond in order to develop the desired properties in terms of strength & durability. A good curing practice involves keeping the concrete damp until the concrete is strong enough to do its job .
However, good curing practices are not always religiously followed in
most of the cases, leading to a weak concrete. This article summarizes
various aspects of curing of concrete which can be of valuable
assistance in adopting good construction practices at site.
.
However, good curing practices are not always religiously followed in
most of the cases, leading to a weak concrete. This article summarizes
various aspects of curing of concrete which can be of valuable
assistance in adopting good construction practices at site.
Curing of concrete must begin as soon as possible after placement & finishing and must continue for a reasonable period of time as per the relevant standards, for the concrete to achieve its desired strength and durability. Uniform temperature should also be maintained throughout the concrete depth to avoid thermal shrinkage cracks. Also protective measures to control moisture loss from the concrete surface are essential to prevent plastic shrinkage cracks.
In a nut shell, curing process is designed primarily to keep the concrete moist by controlling the loss of moisture from the body of concrete, during the given period in which it gains strength.
IS-456:2000 provisions for duration of Curing (Indian Standard-Plain & Reinforced concrete-Code of Practice, 4th revision, page 27)
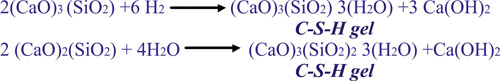
Exposed surfaces of concrete shall be kept continuously damp or in a wet condition by ponding or by covering with sacks, canvas, hessian or other similar material and kept continuously wet for atleast 7 days from the date of placing, in case of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and atleast 10 days when mineral admixtures or blended cements are used. In case of concrete where mineral admixtures or blended cements are used, it is recommended that the above minimum periods may be extended to 14 days, for assisting the secondary reaction.
Water Curing
- is done by spraying or sprinkling water over the concrete surface to
ensure that the concrete surface remains continuously moist. This
prevents the moisture from the body of concrete from evaporating and
contributes to the strength gain of concrete. 
Concrete failures at site are associated to several reasons; right from concrete mix design, properties of materials used, mixing, placing, compaction, curing procedures and many more. There are many misconceptions about the duration of curing of concrete, especially when we refer to site conditions. On many occasions, it is found that the curing period of concrete elements, plasters, brickwork, etc is left to the discretion of the site staff. Improper curing is considered as one of the significant reasons for concrete failures in columns, beams, slabs, pavements, etc, evident in the form of cracks, which are easily noticeable by the naked eyes. The vertical member like a column, in particular, is one of the most victimized RCC elements which must be carefully cured, as the entire load from the slabs and beams are supported by columns and transferred to the foundations. Unfortunately, adequate curing is not given much importance at most of the sites leading to reduction in the durability of the structure.
Curing of concrete plays a major role in developing the microstructure and pore structure of concrete. Curing of concrete means maintaining moisture inside the body of concrete during the early ages and beyond in order to develop the desired properties in terms of strength & durability. A good curing practice involves keeping the concrete damp until the concrete is strong enough to do its job
 .
However, good curing practices are not always religiously followed in
most of the cases, leading to a weak concrete. This article summarizes
various aspects of curing of concrete which can be of valuable
assistance in adopting good construction practices at site.
.
However, good curing practices are not always religiously followed in
most of the cases, leading to a weak concrete. This article summarizes
various aspects of curing of concrete which can be of valuable
assistance in adopting good construction practices at site.Importance of Curing
Curing is the process of controlling the rate and extent of moisture loss from concrete to ensure an uninterrupted hydration of Portland cement after concrete has been placed and finished in its final position. Curing also ensures to maintain an adequate temperature of concrete in its early ages, as this directly affects the rate of hydration of cement and eventually the strength gain of concrete or mortars.Curing of concrete must begin as soon as possible after placement & finishing and must continue for a reasonable period of time as per the relevant standards, for the concrete to achieve its desired strength and durability. Uniform temperature should also be maintained throughout the concrete depth to avoid thermal shrinkage cracks. Also protective measures to control moisture loss from the concrete surface are essential to prevent plastic shrinkage cracks.
In a nut shell, curing process is designed primarily to keep the concrete moist by controlling the loss of moisture from the body of concrete, during the given period in which it gains strength.
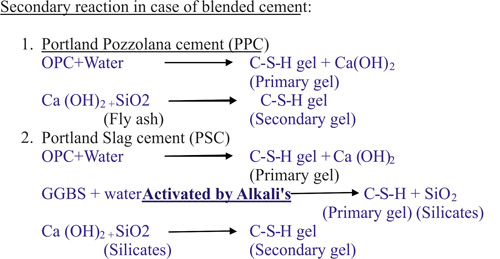
Reasons to Cure Concrete
There are several important reasons why one should cure concrete: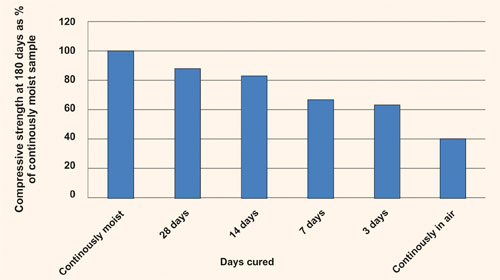 |
| Figure 1: Effect of duration of water curing on strength of concrete(CCAA, data sheet, April 2006, figure-1, page2) |
- Concrete strength gain - Concrete strength increase with age as moisture and a favorable temperature is present for hydration of cement. An experimental investigation was conducted by "Cement, Concrete & Aggregates Australia" (CCAA) and the same was published in their data sheet on "Curing of Concrete," which has been included in this article for reference. Figure-1 illustrates a comparison of the strength of concrete at 180 days of moist curing with various periods of moist curing (0, 3, 7, 14 & 28 days) and then allowing it to dry out. From the graph below, it can be observed that concrete allowed to dry out immediately, achieves only 40% of the strength of the same concrete water cured for the full period of 180 days.
- Improved durability of concrete – The durability of concrete is affected by a number of factors including its permeability, porosity and absorptivity. Well cured concrete can minimize thermal, plastic & drying shrinkage cracks, making concrete more water tight, thus preventing moisture and water borne chemicals from entering into the concrete and thereby increasing its durability.
- Enhanced serviceability - Concrete that is allowed to dry out quickly undergoes considerable early age shrinkage. Inadequate curing contributes to weak and dusty surfaces having a poor abrasion resistance.
- Improved microstructure - Material properties are directly related to their microstructure. Curing assists the cement hydration reaction to progress steadily and develops calcium silicate hydrate gel, which binds the aggregates leading to a rock solid mass, makes the concrete denser, decreases the porosity and enhances the physical and mechanical properties of concrete.

Right Time to Cure Concrete
- After concrete has been placed in its final position and during the initial set, bleed water rises to the concrete surface as plastic settlement occurs. During this period, if the rate of evaporation of bleed water is greater than the rising water, plastic shrinkage of the concrete occurs. Initial mist curing is necessary to keep the surface moist to prevent the surface from drying out.
- Between initial set and final set, intermediate curing would be needed if the finishing is complete prior to final set. This may be in the form of a barrier which prevents the loss of moisture from the concrete surface. e.g. covering the concrete surfaces with plastic sheets, waterproof paper, etc.
- After final set, meticulous curing will have to be done as per the procedures selected. e.g. water curing methods-Ponding, Misting, wet coverings with hessian cloth, Impermeable membrane curing, Curing compounds, etc.
Duration of Curing
The duration of curing of concrete depends on the grade & type of cement, mix proportion, desired concrete strength, shape and size of the concrete member and environmental & exposure conditions. The duration may vary from few days to a month.IS-456:2000 provisions for duration of Curing (Indian Standard-Plain & Reinforced concrete-Code of Practice, 4th revision, page 27)
Exposed surfaces of concrete shall be kept continuously damp or in a wet condition by ponding or by covering with sacks, canvas, hessian or other similar material and kept continuously wet for atleast 7 days from the date of placing, in case of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and atleast 10 days when mineral admixtures or blended cements are used. In case of concrete where mineral admixtures or blended cements are used, it is recommended that the above minimum periods may be extended to 14 days, for assisting the secondary reaction.

Methods to Cure Concrete
Methods of curing concrete broadly fall into the following categories:- Water curing-preventing the moisture loss from the concrete surface by continuously wetting the exposed surface of concrete.
- Membrane curing-minimizing moisture loss from the concrete surface by covering it with an impermeable membrane.
- Steam curing-keeping the surface moist and raising the temperature of concrete to accelerate the rate of strength gain.
 |
| Figure 2: Mist curing of freshly placed concrete |
- Ponding This is the most common and inexpensive method of curing flat surfaces such as floor slabs, flat roofs, pavements and other horizontal surfaces. A dike around the edge of the slab, which may be sub-divided into smaller dikes, is erected and water is filled to create a shallow pond. Care must be taken to ensure that the water in the pond does not dry up, as it may lead to an alternate drying and wetting condition.
- Sprinkling, fogging & mist curing: Using a fine spray or fog or mist of water can be an efficient method of supplying water to the concrete surface especially during hot weather, which helps to reduce the temperature of concrete, eventually conserving moisture inside the body of concrete.
- Wet coverings: Water absorbent fabrics such as hessian, burlaps, cotton mats, rugs etc. may be used to maintain water on the concrete surface by completely covering the surface immediately after the concrete has set. They must be continuously kept moist to prevent the fabric from absorbing water from the body of concrete, due to capillary action.







0 comments:
Post a Comment